Understanding Eczema Signs: Recognizing the Symptoms
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that can cause significant discomfort. It typically manifests as dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
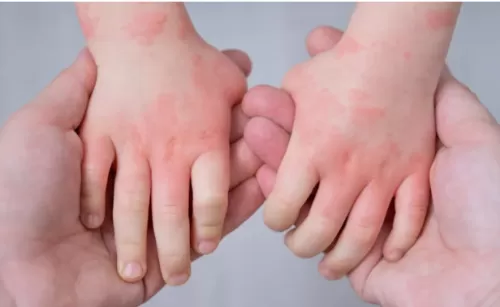
Recognizing the signs of eczema early can lead to effective management and relief. In this article, we’ll explore the key signs of eczema and what to look for.
1. Itchy Skin
One of the most prominent signs of eczema is intense itching. This can range from mild to severe and often worsens at night. The urge to scratch can lead to a cycle of irritation and inflammation, making the condition worse.
2. Dry, Flaky Skin
Eczematous skin tends to be dry and can appear scaly or flaky. This dryness is a result of a compromised skin barrier, which allows moisture to escape and irritants to enter. Keeping the skin moisturized is crucial in managing this symptom.
3. Red or Brownish-Gray Patches
Eczema often presents as red, inflamed patches on the skin. In individuals with darker skin tones, these patches may appear brownish or grayish. These areas can develop on various parts of the body, including the face, neck, elbows, and behind the knees.
4. Thickened, Cracked Skin
Chronic scratching and irritation can lead to lichenification, where the skin becomes thickened and leathery. This can result in cracks that may bleed or become infected, further complicating the condition.
5. Small, Raised Bumps
In some cases, eczema can cause small, raised bumps that may ooze or crust over when scratched. These bumps can appear on the arms, legs, and other areas of the body.
6. Sensitive Skin
Eczematous skin can become hypersensitive, reacting negatively to various substances, including soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics. This sensitivity can exacerbate symptoms, making it essential to choose gentle, hypoallergenic products.
7. Swelling
Inflammation associated with eczema can lead to swelling in the affected areas. This swelling may accompany redness and discomfort, making the skin feel warm to the touch.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of eczema is the first step toward effective management. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can help alleviate discomfort and improve skin health, allowing you to enjoy a better quality of life. Remember, managing eczema often involves a combination of skincare routines, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatments, tailored to your individual needs.

